Detection and Prevention of Cyberbullying on Social Media
Cyberbullying, a pervasive issue in the digital age, involves the use of technology to harass, threaten, or embarrass others. Social media platforms, with their vast user base and real-time communication, have become fertile ground for cyberbullying. This article will delve into the detection and prevention strategies to combat this harmful behavior.
Understanding Cyberbullying
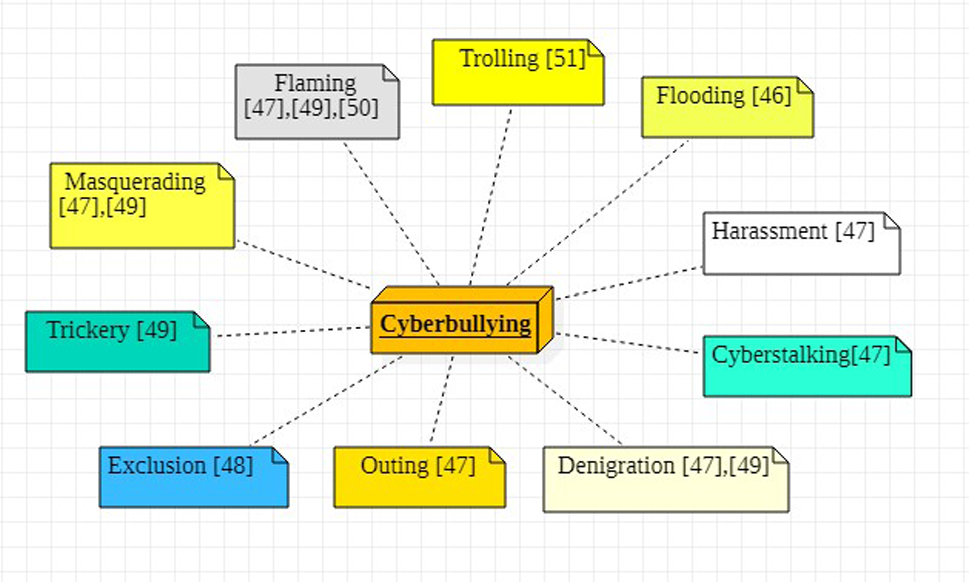
Cyberbullying can take various forms, including:
- Flaming: Sending hostile or insulting messages.
- Denigration: Posting negative or false information about someone.
- Impersonation: Creating fake profiles to harass others.
- Outing: Sharing private information without consent.
- Exclusion: Intentionally excluding someone from online groups or activities.
Challenges in Detection
Detecting cyberbullying is complex due to several factors:
- Anonymity: Many users can remain anonymous online, making it difficult to identify perpetrators.
- Volume: The sheer volume of content on social media platforms makes manual monitoring impractical.
- Subjectivity: Determining what constitutes bullying can be subjective, as it often involves context and intent.
- Evolving Tactics: Cyberbullies constantly adapt their methods, making it challenging to keep up with new trends.
Detection Techniques
-
Keyword-based Detection:
- Identifying keywords or phrases associated with bullying behavior (e.g., “loser,” “ugly,” “stupid”).
- Limitations: Can lead to false positives and may not capture more subtle forms of bullying.
-
Machine Learning:
- Training algorithms to recognize patterns in language and behavior indicative of bullying.
- Approaches include:
- Natural language processing (NLP) to analyze text content.
- Sentiment analysis to detect negative emotions and intent.
- Anomaly detection to identify unusual or suspicious behavior.
-
Social Network Analysis:
- Examining the relationships between users and identifying patterns of abuse or harassment within social networks.
- Limitations: May require significant data and computational resources.
-
User Reporting:
- Encouraging users to report instances of bullying through dedicated reporting mechanisms.
- Limitations: Relies on user awareness and willingness to report.
Prevention Strategies
-
Education and Awareness:
- Providing education on cyberbullying to users of all ages, emphasizing the harmful consequences and promoting respectful online behavior.
- Developing curriculum for schools and online resources for parents and caregivers.
-
Community Guidelines and Enforcement:
- Establishing clear guidelines prohibiting cyberbullying and enforcing them consistently.
- Utilizing a combination of automated tools and human moderators to review and remove harmful content.
-
User Empowerment:
- Empowering users to take control of their online experience by providing tools for blocking, muting, and reporting abuse.
- Encouraging users to use privacy settings to limit the visibility of their personal information.
-
Collaboration with Law Enforcement:
- Working with law enforcement agencies to investigate and prosecute serious cases of cyberbullying.
- Establishing clear protocols for reporting and responding to incidents.
-
Research and Innovation:
- Continuously researching new detection and prevention techniques to stay ahead of evolving threats.
- Investing in innovative technologies to enhance the ability to identify and address cyberbullying.
Additional Considerations for Cyberbullying Prevention
While the strategies discussed above are essential, it’s important to consider other factors that can contribute to the prevention and mitigation of cyberbullying:
1. Parental Involvement:
- Educating Parents: Provide parents with resources and information about cyberbullying prevention.
- Monitoring Online Activity: Encourage parents to monitor their children’s online activities and have open conversations about safe internet use.
- Setting Boundaries: Help parents set appropriate boundaries for their children’s online time and access to content.
2. School Policies and Programs:
- Comprehensive Policies: Develop clear policies and procedures to address cyberbullying incidents.
- Education and Awareness: Incorporate cyberbullying prevention education into school curricula.
- Support Services: Provide counseling and support services for victims of cyberbullying.
3. Cultural and Social Factors:
- Addressing Stigma: Challenge negative stereotypes and stigma associated with being a victim of cyberbullying.
- Promoting Empathy and Respect: Foster a culture of empathy and respect both online and offline.
- Addressing Social Inequalities: Recognize and address social inequalities that may contribute to cyberbullying.
4. Technology and Innovation:
- Advanced Detection Tools: Continue to invest in research and development of innovative tools to detect cyberbullying more effectively.
- Privacy and Security: Prioritize privacy and security measures to protect user data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Ethical AI: Ensure that AI-powered detection tools are developed and used ethically, respecting privacy and avoiding discrimination.
5. International Cooperation:
- Global Standards: Develop international standards and guidelines for addressing cyberbullying.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Foster collaboration between governments, technology companies, and organizations to combat cyberbullying on a global scale.
Conclusion
Cyberbullying is a serious issue that requires a multifaceted approach to combat it effectively. By combining detection techniques, prevention strategies, and collaboration, we can create safer and more inclusive online environments for everyone. It is essential for social media platforms, users, and communities to work together to address this pressing challenge and protect individuals from harm.