http error 500.30 – asp.net core app failed to start You finally push your ASP.NET Core app live, sit back, refresh the browser—then boom. You’re hit with a cryptic message: HTTP Error 500.30 – ASP.NET Core app failed to start. If you’re scratching your head, you’re not alone. This is a common error that plagues many developers, especially during deployment.
So what exactly does it mean? And how do you fix it fast?
Let’s break it down step-by-step so you can squash the bug and get back to building.
What Causes HTTP Error 500.30?
Common Triggers
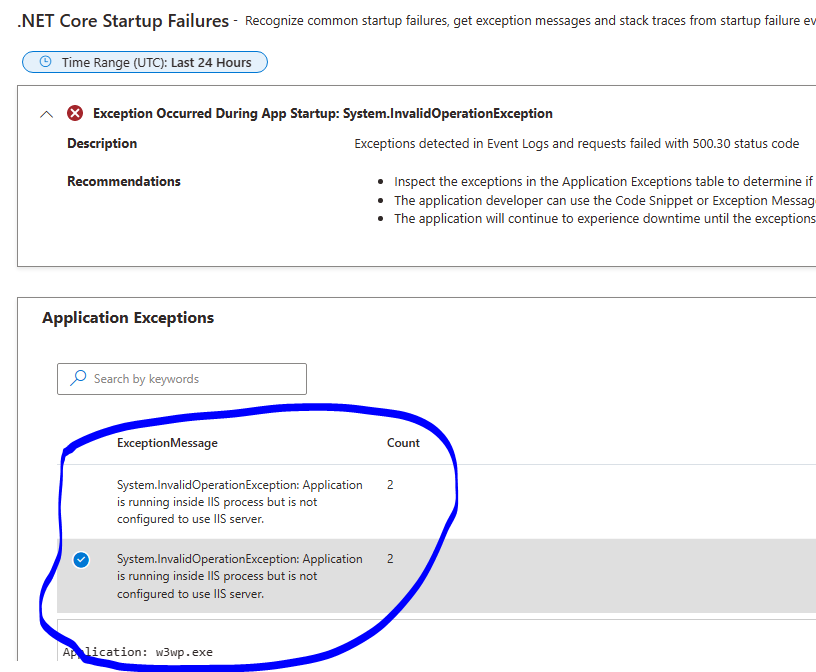
This error usually pops up when the app crashes before it can fully start. Here’s what might be going on:
-
Runtime exceptions during startup.
-
Invalid code in the
Startup.csorProgram.csfiles. -
Missing configuration files or environment variables.
Hosting Issues
Your hosting setup could also be the culprit. If you’re using IIS or Azure App Services and something isn’t configured right, you’re bound to face this error.
Breaking Down the Error Message
What the Error Looks Like
Typically, the browser shows:
This message doesn’t give much detail, but there’s usually more info in the logs or stdout log file.
Interpreting Stack Traces
When you check logs or run the app from the terminal, you might get a stack trace pointing to exactly where the crash occurred—super helpful!
Deployment Pitfalls That Cause 500.30
Missing Environment Variables
If your app relies on ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT, database connection strings, or third-party keys, and they’re not set on the server, it may refuse to start.
Incorrect Web.config Settings
A misconfigured web.config file can prevent IIS from properly launching your app through the ASP.NET Core Module.
.NET Runtime Not Installed
Your server needs the correct .NET Core or .NET version installed. Without it, your app is dead in the water.
Diagnosing the Problem
Using Logs
Check the logs folder in your published directory or enable the stdoutLogFile in your web.config file. Logs often reveal the root cause.
Checking Event Viewer
On Windows servers, the Event Viewer can show application-level errors under Windows Logs > Application.
Dotnet CLI Commands
Run:
This gives you live error output, letting you debug without relying on IIS.
Solutions and Fixes
Enable stdoutLogFile
In web.config, update:
This logs all startup issues in a readable file.
Fixing Broken Startup.cs
This is the first place to check. One wrong method call or bad dependency injection setup and boom—your app fails to boot.
Reinstalling .NET Core Hosting Bundle
If the server is missing the right runtime, install or repair the .NET Core Hosting Bundle.
Prevention Strategies
Pre-Deployment Checklist
-
Ensure
appsettings.jsonand secrets are correct. -
Confirm correct
.NET versionis installed. -
Set necessary environment variables.
Use Application Insights or Logging
Real-time logging and telemetry can help you catch issues before users do.
Advanced Debugging Tips
Enabling Developer Exception Page
Temporarily enable the developer exception page in Startup.cs:
Using Visual Studio Remote Debugging
Attach to the process remotely using Visual Studio to see exactly where your app crashes during startup.
Hosting Environment Considerations
Development vs. Production
You can switch environments by setting:
Just don’t forget to switch back for production!
How AppSettings Differ by Environment
Use appsettings.Development.json or appsettings.Production.json to load different configs based on the environment.
Real-World Examples
Case Study 1: Web.Config Gone Wrong
One developer deployed a perfectly working app locally—but forgot to set stdoutLogEnabled in web.config. Debugging was blind until they turned it on and discovered a typo in Startup.cs.
Case Study 2: Startup.cs Crash
Another team hit 500.30 after injecting a service before registering it in DI. One line change in ConfigureServices fixed everything.
Community Resources and Tools
Stack Overflow and GitHub
Searching for your error message verbatim often leads to solutions from developers who’ve been in your shoes.
Microsoft Documentation
Microsoft’s official docs have detailed deployment and troubleshooting guides.
Conclusion
HTTP Error 500.30 can be frustrating, but it’s fixable with the right troubleshooting mindset. Start with logs, look at your Startup.cs, and ensure your hosting environment is correctly configured. Most importantly, don’t panic. Every error is a learning opportunity, and now you’re armed with the tools to handle it like a pro.